I. Definitions and key concepts
What is the skills and versatility matrix?
The skills matrix is a tool for mapping and assessing the specific skills of each employee within an organization. These may be technical skills (hard skills), behavioral skills (soft skills) or domain- or industry-specific skills. This matrix helps identify team strengths and weaknesses, plan training and development, and align employee skills with corporate objectives.
On the other hand versatility matrix is a tool for assessing and visualizing each employee's ability to perform various tasks or roles within the organization. It measures employees' flexibility and adaptability, and can help identify those who can be trained to take on multiple or interchangeable roles. This matrix can help improve team resilience and efficiency, by enabling better task allocation and providing cover in the event of absence or role change.
What's the difference between a skills matrix and a versatility matrix?
The skills matrix and the versatility matrix have complementary purposes, but they don't meet the same business needs.
Visit skills matrix focuses on what each employee can do It allows you to view skills required for each position and measure the level of skill mastery among employees. This tool helps HR teams and managers identify gaps between available skills and the company's needs. It is a valuable basis for building a development plan training, individual support, mission development...
At the same time versatility matrix is more interested in employees' ability to perform multiple roles or to intervene on different tasks. It reflects the operational flexibility and adaptability of a team. This tool is often used to secure business: it facilitates the management of absences, workload peaks or organizational changes, by quickly identifying who can take over a given task or position.
In a nutshell:
- The matrix of skills is essential to manage technical and behavioral skills, and to support skills upgrading through targeted development plans.
- The matrix of versatility is a lever for organization and resilience, guaranteeing business continuity in the event of unforeseen events.
Used together, these two matrices become powerful tools for optimizing both talent development and operational efficiency.
II. Why build a skills and versatility matrix?
Regulations and quality (ISO 9001 certification))
Building a matrix of skills and versatility is essential to meet the needs of our customers. regulatory and quality requirementsparticularly in the context of ISO 9001 certification.
This international standard, dedicated to quality management systems, requires organizations to identify the following skills required for positions that have an impact on product or service conformity. It also requires measuring existing skillsand implement a development plan to maintain and reinforce these skills over the long term.
The skills and versatility matrix plays a crucial role in this process. It provides an overview of the skills available within the organization, and highlights areas where action is needed to fill gaps. The use of this matrix not only helps to ensure the organization's compliance with ISO 9001 standardIt also contributes to improving the overall performance of the quality management system.
Authorization tracking
Visit authorization tracking is another major reason why building a skills and versatility matrix is essential in any organization. Clearances are the formal authorizations granted to employees to perform certain tasks or operate certain machines or equipment, often based on their training and experience.
A skills and versatility matrix enables these authorizations to be tracked and managed efficiently. It provides an overview of which employees have the necessary skills and clearances to perform specific tasks, facilitating optimal task allocation.
In addition, it helps identify employees who may require additional training to obtain certain clearances, or those whose clearances are about to expire and need to be renewed. In this way, the skills and versatility matrix becomes an invaluable tool for ensuring the company's compliancesafety and operational efficiency.
Securing know-how and passing it on
Securing know-how and passing it on is another imperative for which organizations need to develop a skills and versatility matrix. Know-how, which represents the specific expertise accumulated by employees over time, is a valuable asset for any company. However, this capital can be at risk, particularly when a key employee leaves the organization. A skills and versatility matrix helps to identify and secure this know-how by determining precisely who possesses which skills or expertise within the company. It also facilitates planning succession planning and skills transfer by identifying potential replacements for each key position.
In addition, by highlighting existing skills and those that need to be developed, the matrix helps to design effective training plans to ensure the transmission of know-how. In this way, the skills and versatility matrix plays a decisive role in ensuring the continuity and resilience of the company, by securing its knowledge capital.
Set up a training plan
A training plan is based on a clear understanding of existing skills and potential areas for improvement within the team. A skills and versatility matrix provides a clear view of these elements, identifying not only the skills currently held by employees, but also those that may require further development. This enables training managers to create targeted, relevant programs that meet the organization's real needs.
In addition, the matrix can help identify employees who could benefit most from certain training courses, or those who could serve as in-house trainers thanks to their expertise in certain areas. In this way, the use of a skills and versatility matrix can significantly improve the effectiveness and impact of training initiatives.
Support for recruitment
Recruitment is another area where the development of a skills and versatility matrix is crucial. In today's intense competition for talent, it's essential for organizations to understand exactly what skills they need to achieve their objectives. A skills and versatility matrix provides an overview of existing skills within the organization, and highlights gaps that may require recruitment. This enables hiring managers to target more precisely the skills required when looking for new talent.
Furthermore, by highlighting skills that are in short supply within the organization, the matrix can help identify positions for which it might be beneficial to offer in-house training, rather than seeking to recruit from outside. In this way, a skills and versatility matrix can provide valuable support for recruitment, helping to align the recruitment strategy with the organization's real needs.
👉 Saint-Gobain shares its experience: how to switch from paper dies to digital tools with Mercateam.
III. How to create a skills matrix
Creating a skills and versatility matrix is not a task to be taken lightly; it's a strategic process that can transform the way you manage your talent and drive your organization. Here are the key steps to building a robust and effective skills matrix.
Identify key skills and areas of versatility
The first step in building your skills matrix is to identify the key skills and areas of versatility required in your organization. These are the technical and functional skills that are crucial to achieving your objectives. It can be useful to work closely with the managers of each department to determine the specific skills required for each position. Don't forget to consider "soft" skills, such as communication and problem-solving, which are just as important to your organization's success.
Assessing skill levels and versatility
Once you've identified the key competencies, the next step is to assess the skill level and versatility of each member of your team. This can be done through individual interviews, performance appraisals or skills tests. The aim is to understand not only whether an individual possesses a particular skill, but also how competent and versatile they are in that area.
Structuring the matrix
The third step is to structure the matrix itself. This involves creating a grid where each row represents a team member and each column represents a key skill. The point of intersection between a row and a column should indicate that individual's level of competence in that particular area. Versatility can be represented by adding an extra dimension to the matrix to indicate the number of skills in which each individual is proficient.
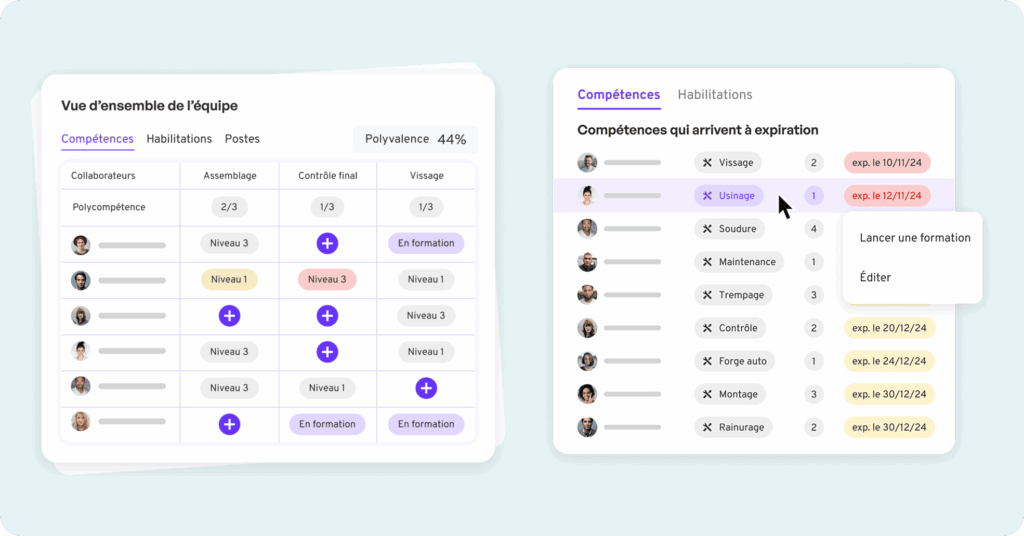
Manage data and update the matrix
Last, but by no means least, is data management and updating the matrix. Skills and organizational needs evolve over time, so it's crucial to regularly update the matrix to keep it relevant. This may involve reassessing employees' skills at regular intervals, adding new skills to the matrix as they become relevant, or reviewing existing skills to ensure they are still aligned with the organization's objectives.
Building a skills and versatility matrix is no simple task, but the benefits it can bring to your organization are immense. With a well-designed skills matrix, you'll be better equipped to manage your talent, plan your training, and lead your organization to success.
IV. Why use skills management software rather than Excel?
Skills management is a major concern for organizations, and can be complex without the right tools. While many turn to ExcelHowever, there are many reasons why opting for dedicated skills management software, such as that offered by Mercateam, is a more sensible solution.
Continuous data updates
Mercateam offers automatic, real-time data updates, unlike Excel which requires manual updating. This can become a tedious task, and the matrix can quickly become obsolete if not regularly updated.
Collaboration made easy
Unlike Excel, competency management software like Mercateam is an intrinsically collaborative tool. It simplifies the sharing of information and documents, enabling smooth collaboration between team members.
Process integration
Mercateam offers the possibility of integrating different processes within a single platform. This makes it possible to map skills, launch 360° assessments, allocate training, track authorizations, and much more.
Data security
Skills management software, including Mercateam, is designed with strict security protocols to protect your data. This means they can encrypt your data, control who has access to it, and monitor suspicious activity. In a context where data breaches are a major concern for businesses, this functionality is essential. In contrast, although Excel can be password-protected, it doesn't offer the same level of security and is more vulnerable to human error, such as accidentally sharing files containing sensitive information.
Customization
Every organization has its own unique skills management needs. Competency management software, such as Mercateam, can generally be tailored to meet these specific needs. For example, you can configure the software to track and assess competencies that are particularly important to your organization, define specific competency assessment processes, or customize the reports and analyses generated by the software.
Whether your organization is large or small, Mercateam helps you to effectively manage skills matrices and employee authorizations, ensuring that your organization has the right people in the right jobs at all times. Choosing Mercateam over Excel for competency management means opting for a dynamic, collaborative and integrated tool, capable of meeting the specific needs of your organization.



