What is industry?
Industry is a key sector of the economy, encompassing all activities dedicated to the large-scale production of goods and services. It plays a central role in the development of societies, providing the resources and products needed for daily life, innovation and growth. Industry is distinguished by its ability to transform raw materials into finished products, thanks to increasingly sophisticated production processes. Over time, this sector has undergone major transformations, driven by technological advances and automation, which have increased productivity and optimized industrial activities. Today, industry is in a perpetual state of change, integrating digital advances to meet new economic, social and environmental challenges.
Evolving industrial concepts
Industrial concepts have evolved profoundly over the centuries, driven by the various industrial revolutions. Each revolution marked a turning point in the way production processes were conceived and emerging technologies integrated. The fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0, has introduced major innovations such as. the Internet of Things (IoT)This has led to the emergence of new technologies, such as computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), artificial intelligence (AI) and big data, enabling advanced automation and intelligent data management. Today, Industry 5.0 takes up the baton, focusing on collaboration between humans and machines, promoting the personalization of products and services. This new concept aims to put people back at the heart of industry, valuing creativity, expertise and adaptability, while harnessing the power of technology to create more flexible, innovative and responsible production processes.
Industry 1.0 - The age of steam and coal
At the end of the XVIIIᵉ century, the first industrial revolution profoundly transformed the world. France's industrial fabric and the start of a major European transformation. Coal-fired steam engines gradually replaced human and animal power.
In the industrial sector mechanized looms increased productivity eightfold. Visit industrial plants are developing around the big cities and overturning thework organization.
This period also marks the beginning of a business model focused on industrial production and the rise of new sectors as the steel industry or the refining.
Industry 2.0 - Electrification and mass production
At the beginning of the XXᵉ century, the robotization does not yet exist, but theelectrification and Henry Ford's invention of the assembly line in theautomotive industry enable large-scale production.
The manufacturing output becomes standardized: the production lines improve competitiveness and reduce costs, making goods more affordable.
The flexibility ofproduction equipment thanks to the use of electric motors, paving the way for new industrial sectors as theaeronautics and theagri-food.
Industrie 3.0 - Automation and IT
From the 1970s onwards, factories entered the era of theautomation thanks toITPLCs and industrial robots.
The data collected on the machines are analyzed to optimize industrial performance and reduce breakdowns.
It was also the start of the ERP and production management computer-assisted help identify and anticipate maintenance needs.
Visit industrial companies are starting to integrate training plans to maintain specific skills required for maintenance and programming.
Industrie 4.0 - Intelligent and connected factory
Now widely deployed in manufacturing industries, l'industry 4.0 marks a major technological milestone in the digitization, automation and integration of advanced technologies such asIndustrial Internet of Things (IoT), l'artificial intelligence (AI) and collaborative robotics in industrial processes. This harmonious integration of technology optimizes production, improves energy efficiency and enhances human-machine collaboration, a key aspect of data security and overall industrial system performance.
- L'Industrial Internet of Things (IoT)
- L'artificial intelligence and the Big Data
- Visit platforms collaborative
- The augmented reality and digital simulation
- The supply-chain connected
L'artificial intelligence and theartificial intelligence (AI) play a central role in automation, process optimization, predictive maintenance and improved decision-making thanks to real-time data analysis. Industry 4.0 is thus transforming the industrial system by integrating people into an advanced technological environment, where digitalization facilitates rapid, informed decision-making.
These technologies help to identify performance gaps, improve flexibility, customize production while reducing the environmental footprint, and maximize overall efficiency. They also offer innovative solutions for business continuity and product customization, responding to specific business needs.
Industrial transformation relies not only on technology, but also on close collaboration with suppliers and partners throughout the supply chain. These collaborations promote transparency, sustainability and supply-chain optimization, while ensuring compliance with ethical and environmental standards.
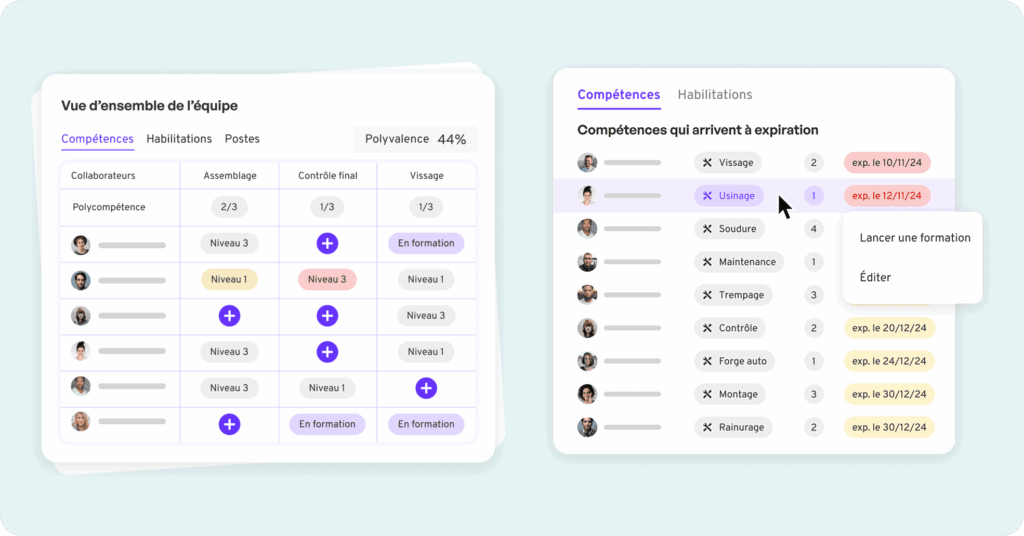
Implementing digital tools for industrial skills management is becoming essential: a skills plan is a key tool for linking digital transformation objectives to team skills development.
🎯 Request a free demo of Mercateam software
Characteristics of today's industry
Today's industry is characterized by profound digital transformation and unprecedented connectivity. The integration of big data, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things into industrial processes is helping to optimize productivity, improve product quality and enhance operational efficiency. This industrial era is also characterized by a growing awareness of the challenges of social responsibility and sustainability. Industrial companies are increasingly committed to initiatives aimed at reducing their environmental impact, guaranteeing the safety and well-being of their employees, and meeting the expectations of their stakeholders. Modern industry is no longer content with technological innovation: it is placing transformation, sustainability and social responsibility at the heart of its strategy, in order to build a more respectful and efficient industrial future.
Industrie 5.0 - The inclusive, sustainable factory
L'industry 5.0 represents the fifth industrial revolution, marking a major evolution centred on thehuman and the responsible integration of advanced technologies. This new phase places people at the heart of industrial processes, encouraging collaboration between workers and machines for greater customization and creativity. Visit pillar humanocentricity of Industry 5.0 is to put people back at the heart of the process. system industry, based on pillars resilience, sustainability, human-centricity and innovation. Visit principles of Industry 5.0 are based on social responsibility, environmental sustainability and the synergy between technology and people.
Objectives:
- Strengthen man-machine cooperation (collaborative robots, exoskeletons, intelligent sensors), a aspect key to improving decision-making and theefficiency processes.
- Reduce our environmental impact (circular economy, reduced energy consumption), by making sustainable development a central axis of industrial transformation.
- Enhance industrial trades and strengthen theattractiveness based on solutions innovative and responsibleartificial intelligence and others technologies advances.
- Update continuous industrial skills thanks to professional training and development planswhile promoting collaborations with ethical partners and suppliers responsible.
The european commission plays a key role in defining the societal and environmental objectives of Industry 5.0, underlining the dimension European of this transition to a more sustainable and innovative industrial model. Industry 5.0 thus represents a answer to today's social and environmental challenges, by transforming the system to meet society's expectations.
The installation strategy forward-looking management of jobs and skills (GPEC) is a major lever in supporting this transformation. Visit French companies that will succeed in combining industrial innovation, operational flexibility and added value will have a sustainable competitive advantage in a globalized market.
Finally, it is essential to ask the question question How can Industry 5.0 improve quality of life, enhance sustainability and meet social challenges? These questions to reflect on the impact of this industrial revolution, and on the ways in which answers for a more responsible future.
Accelerated transition: from 1.0 to 5.0
Previous cycles took decades. However, the rapid transition between different industrial revolutions, notably from 4.0 to 5.0 industrialization, marks a profound transformation in working methods. In contrast, the rise of digital technology digital transformationIndustrialization 4.0, then 5.0 have followed one another in less than two decades. The harmonious integration of technologies such as IoT, AI and robotics is facilitating this transition and promoting man-machine collaboration. Technological convergence (Big Data, AI, IoT) today enables us to go beyond automation: it improves the overall efficiency of industrial processes, while accelerating decision-making thanks to digitalization. Last but not least, innovative, customized solutions support companies in their transition to Industry 5.0.
Why start now?
- For identify key skillsbuild a development plan, create a skills matrixand theintegrate with business processesinnovative solutions for optimizing skills management and improving process efficiency.
- The structuring of industrial professions requires rapid, well-informed decision-making to adapt skills to technological and organizational changes.
- Improving efficiency in skills and process management is key to increasing productivity while reducing costs.
- It is also crucial to integrate the principles of sustainable development into the structuring of industrial professions, in order to meet today's environmental and social challenges.
- Finally, working with suppliers, partners and through responsible collaborations helps to guarantee regulatory compliance, respect ethical standards and strengthen the company's competitiveness.
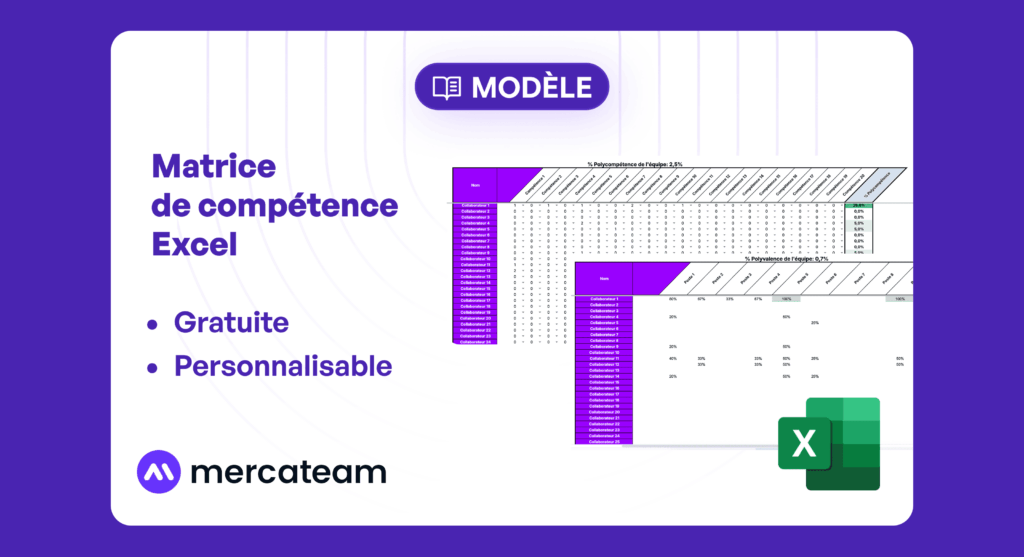
🎯 Download our free Excel skills matrix